Sleep Apnea (OSA) – What is it and how to avoid the risk of complications?
Published 6 Feb 2023 • By Rahul Roy
Sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder that prevents individuals from sleeping peacefully by causing problems with their breathing. It can be difficult to diagnose due to the nature of the symptoms and is more widespread than people realise/realize.
What is sleep apnea? What are its causes and symptoms? What can be done for its treatment? What can be done to reduce the risk of complications with the disorder?
Discover the article here!

What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and restarts while a person is in a state of rest. This can prevent the body from receiving enough oxygen leading to further complications down the line. Although it is not fatal, it could expedite other problems relating to the heart or lungs.
It is a very widespread disease that is very often undiagnosed. It is estimated to affect 5% to 10% of the world population. Men are more likely to be affected by sleep apnea than women. The risk of being affected by the disorder increases the older a person gets and family history can also influence its potential to appear. Other factors that can influence the risk of sleep apnea are being overweight, smoking, drinking alcohol, consuming sleeping pills before sleep and the presence of respiratory diseases such asthma.
1.5 million adults in the UK are believed to be affected by sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
The symptoms of sleep apnea can easily be confused as commonplace issues that affect everyone, but persistent appearance of these symptoms is a cause for worry. In this case, it is recommended to visit a doctor for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Some of the most common symptoms are -
- Loud snoring
- Deep pauses during sleep that may only be visible to a partner, or another loved one
- Tiredness and fatigue during the day
- Repeatedly waking up at night
- Waking up with a headache or a dry mouth or both
- General irritability coupled with mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating and paying attention during the day
- Sweating profusely at night
- Sexual dysfunction
Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can be broadly classified into 3 types. They have very similar symptoms that can sometimes be confused with each other. They are-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
This is the most common type of sleep apnea disorder. It occurs when the muscles and neck relax during the sleeping state, causing the throat muscles to press on the windpipe. This blocks airflow into the lungs, causing erratic breathing while sleeping.
Central Sleep Apnea
This is a disorder that occurs due to the brain not sending the right signals to the breathing related muscles, causing them to not function properly. The brain is responsible for always managing breathing, even when a person might be sleeping. When there is a lack of communication between the brain and the breathing muscles, this irregularity happens.
Complex Sleep Apnea
This type of sleep apnea disorder is a combination of the above 2 types, and it occurs when a person with OSA, is treated appropriately (generally with a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine) by the healthcare providers but the problem still persists leading researchers to estimate that it is Central Sleep Apnea. However more research is needed on this disorder.
Treatments for Sleep Apnea
In some situations, sleep apnea can be resolved by making lifestyle choices but most people with the disease have to use the following options-
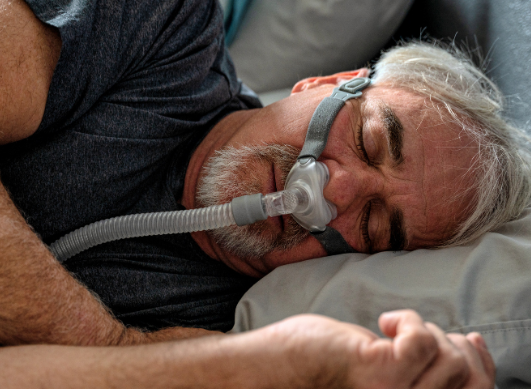
CPAP Machine
This machine gently sends air pressure through a mask which a person wears over the mouth or nose while sleeping. This air pressure helps to exert force on the throat muscles allowing them to remain open and facilitate breathing and better quality of sleep.
Oral Devices
Custom fit oral devices, that work similarly to CPAP machines but with different functionalities, either holding the tongue forward to allow better airflow or holding the jaw in place to prevent airway blockages.
Oral Therapies
There exist therapies such as orofacial therapy that involves exercises for the mouth and facial muscles to strengthen and provide better control.
Surgical Procedures
If the aforementioned procedures don’t work, a patient might require surgery to help improve airflow – by removal of tonsils, to place an implant to monitor breathing, to remove some soft tissue to facilitate easier breathing, etc.
What are the complications with Sleep Apnea
Sleep Apnea is also capable of interfering with other problems that an individual may already have and making them worse-
Blood Pressure
Sleep apnea can negatively impact an individual with high blood pressure. Waking up suddenly in the middle of the night is often very stressful and can trigger the blood pressure of an individual.
Type 2 Diabetes
Sleep apnea is a common disorder faced by individuals with Type 2 diabetes, especially Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). While diet and exercise are often a point of focus for diabetics, sleep is another crucial element that needs to be considered.
Heart related problems
Obstruction of breathing caused by sleep apnea can put people with heart diseases at risk. According to a study, published in the National Library of Medicine, obstructive sleep apnea increases the risk of heart failure by 140%.
Obesity
A person affected by obesity is more at risk of being affected by sleep apnea, and it is estimated that more than 70% of obstructive sleep apnea patients are overweight or obese according to a journal posted in the National Library of Medicine. Weight loss may help to ease the symptoms.
Strokes
Reduced oxygen rich blood flow to the brain by obstructive sleep apnea can increase the risk of having an ischemic stroke, and the more severe the sleep apnea condition, the higher the risk probability for a stroke to occur.
How to avoid the risk of complications?
If diagnosed with sleep apnea or not, these self-care routines could provide some respite from further complicating this disorder-
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise can ease some of the symptoms of sleep apnea and helps contribute to better breathing in general.
Lose excess weight
If overweight or obese, it is important to lose excess weight by practicing an active way of living. A healthy weight can sometimes remedy and ease the symptoms.
Quit smoking
Smoking is injurious to health, especially for the lungs and throat. Look at resources and options that help to wean off tobacco dependence.
Avoid alcohol
Alcohol has the potential to relax some of the muscles in the back of the throat, that could interfere with breathing.
Practice healthy sleeping habits
Try to sleep and wake up at a regular time. Make sure that the room is nice and dark. The more hours of sleep, the better, so try sleeping for 7-8 hours.
Sleep on your side
Sleeping on the side reduces the risk of the tongue and throat muscles blocking the airway passages. This helps ease breathing. Practices like taping a tennis ball to the back or using a pillow as support can help support sleeping on the side.
Final Words
Sleep apnea may seem relatively harmless in the beginning, but it can lead to more serious conditions in the future. Additionally, it can prove problematic for your partner or loved one. That is why it is important to get a medical appointment with a doctor as soon as the early symptoms arise. Don’t take for granted, the sleep that you’ve always wanted!
Did you like this article?
Click on "Like" or share your feelings and questions with the community in the comments below!
Take care of yourself!
Sources:
Sleep apnoea - NHS (www.nhs.uk)
Sleep apnea - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clini(www.mayoclinic.com)
Sleep Apnea - Causes and Risk Factors | NHLBI, NIH (www.nhlbi.nih.gov)
Sleep Apnea: Types, Common Causes, Risk Factors, Effects on Health (webmd.com)
Key Sleep Disorders - Sleep and Sleep Disorders | CDC(www.cdc.gov)
Sleep Apnea: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
Types of sleep apnea: Obstructive, central, and complex (medicalnewstoday.com)
Severe Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Treatment, and More (healthline.com)
Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: Role of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components - PMC (nih.gov)
Comments
You will also like

Fighting schizophrenia symptoms: a long journey against paranoia after detainment and denial
12 Dec 2018 • 7 comments

 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter